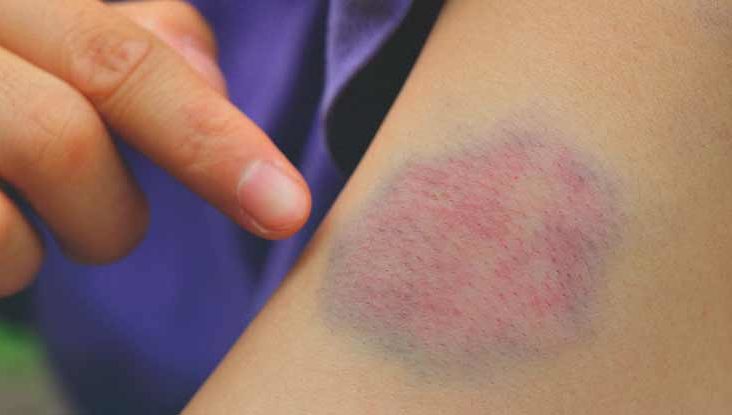
It’s no secret that surgery often leaves a patient with bruising. It can be inconvenient, but it is normal. How does this happen? There are many possible reasons for the occurrence of post-surgery bruising, and understanding them will help you take care of yourself after your surgery in the best way possible. Read on to learn more.
Blood Thinners
Some surgeries require your doctor to use a medication called an anticoagulant. This is most often used in people who have uncontrolled bleeding or serious heart conditions that could cause them to bleed out. These drugs help the blood clot normally, but they also increase the chance of bruising after surgery due to their ability to thin the blood.
During surgery, there is a risk that blood vessels may be cut or damaged. When this happens, it causes bleeding into the tissue around those vessels. Suppose those blood vessels are also being used to support your recovery from surgery. In that case, the result can be excessive swelling and bruising as the body’s inflammatory system kicks in to heal the injury.
Hematomas and Excessive Blood Loss
Sometimes,rhinoplasty surgery can result in a hematoma – an area of internal bleeding – that is not noticed during the operation. This may also cause bruising in rhinoplasty as well as other symptoms such as pain and swelling. It is important to report any such symptoms immediately so that your doctor can remove the hematoma, if it is safe to do so, or take other steps to address the cause of the problem.
The loss of blood can also lead to bruising after surgery. When there is a large amount of bleeding during the procedure, sometimes additional blood has to be made available for transfusion. If this happens and you are taking anticoagulants, be aware that these medications will affect the blood’s ability to clot and can lead to excessive bleeding at the site of a bruise.
Infections
This one is fairly simple. Any microbial infection in the body causes inflammation, which results in an increased risk of bruising. Even a skin infection can result in this side effect when it spreads to deeper layers of tissue underneath the skin.
The IV lines commonly used during surgery can become infected if they have been exposed to bacteria from your skin or unsanitary conditions. This may cause localized bruising and swelling along with fever and other symptoms such as nausea and vomiting.
Some patients bruise more easily after surgery due to a genetic predisposition they have inherited from their parents. Other medical conditions, such as bleeding disorders or inflammatory conditions, can cause people to bruise more often and easily.
Surgery itself
Some surgeries may result in bruises because of the extent of the incision. If a large portion of skin is cut to access an area in the body, there will often be bruising after surgery due to blood vessels being disrupted or damaged.
Those overweight or who have a lot of fatty tissue may notice bruising after surgery due to the surgical procedure involving this fat layer. When it is cut away, blood vessels can be disrupted, and this causes bruising for some patients.
The location of your surgery can also cause bruising that appears weeks later. For example, those who have surgeries on the back or legs will likely notice that they are also bruised in these areas and where the incision was made.
Corticosteroids
Doctors may prescribe corticosteroids before or after surgery to reduce inflammation and swelling caused by tissue damage. These drugs are also known as steroids, which should tell you something about affecting the body’s clotting functions. They interfere with the blood’s ability to clot normally, making it more likely that you will be bruised after surgery if you are taking these medications at the time.
This is especially true for patients who need long-term steroid therapy due to medical conditions like asthma or rheumatoid arthritis. Corticosteroids can affect the body’s natural inflammatory response after surgery, especially if these drugs have been used for a long period before the procedure. Again, this can increase the risk of excessive bruising and other problems such as bleeding and tissue death.
Medications
Many prescription and over–the–counter medications can increase the risk of bruising after surgery or create other complications that will delay recovery. This is especially true if you take more than one of these drugs at a time. For this reason, make sure that you talk with your doctor ahead of time about all medications you are taking before surgery.
While some painkillers, such as acetaminophen and ibuprofen, can cause problems after surgery, others can increase the risk of bleeding or bruising due to their effects on blood clotting. Aspirin and similar anti-inflammatory drugs such as naproxen, ketoprofen, and indomethacin can interfere with blood’s ability to clot normally.
Anesthesia
Local anesthesia, such as that used for dental procedures and small surgeries like an endoscopy, will not cause excess bruising or blood clotting problems. However, general anesthesia can slow or stop the body’s natural functions while the patient is under sedation.
This happens most when you need to be on a ventilator since the breathing machine can interfere with the body’s normal blood oxygenation and carbon dioxide adjustment. If you need to be sedated during surgery, make sure that your doctor knows about any medical conditions you have that affect these functions.
Trauma to the Area under Surgery
The surgery itself can increase the risk of bruising if it causes any tissue trauma or damage to blood vessels in the affected area. This is especially true for surgeries that use heat, light, suction, high pressure, or sharp tools such as needles and scalpels. The surgeon must make some incisions during surgery to reach the affected area.
Some surgeries, such as laser procedures to remove tumors or cauterize blood vessels, can also cause damage by burning tissue and creating scar tissue that decreases the amount of oxygen in the affected area. This condition is known as ischemia, which damages tissues due to reduced blood flow and increased pressure created by swelling around the surgery site.
Bruising after surgery is a common occurrence, but it doesn’t have to be. Once you know the cause, take some steps to reduce your risk.